How to Successfully Implement an ERP System in Your Organization
Introduction
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a major undertaking that can significantly improve business efficiency, data accuracy, and overall performance. However, the success of an ERP implementation hinges on careful planning, effective project management, and clear communication. This article outlines key steps and best practices for successfully implementing an ERP system in your organization.
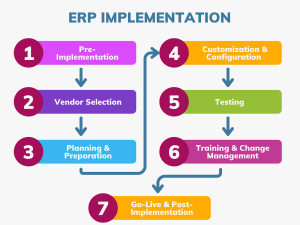
1. Define Clear Objectives and Requirements
Before selecting an ERP system, it’s crucial to define the objectives you aim to achieve with the implementation. These could include improving process efficiency, enhancing data visibility, reducing operational costs, or enabling better decision-making. Engage stakeholders from various departments to gather their input and define specific requirements for the ERP system. This step ensures that the system you choose aligns with your organization’s needs and goals.
2. Choose the Right ERP System
Selecting the right ERP system is critical to the success of the implementation. Evaluate different ERP vendors based on factors such as functionality, scalability, ease of use, and total cost of ownership. Consider whether a cloud-based or on-premises solution is more suitable for your organization. Additionally, assess the system’s ability to integrate with your existing software and processes. It’s often helpful to consult with industry peers or hire a consultant to guide you through the selection process.
3. Assemble a Strong Implementation Team
An effective implementation team is essential for the successful deployment of an ERP system. This team should include a project manager, IT specialists, and representatives from key departments that will use the system, such as finance, operations, and HR. The project manager will oversee the implementation process, ensure that deadlines are met, and address any issues that arise. Departmental representatives will provide insights into how the system can best support their specific needs and processes.
4. Develop a Detailed Implementation Plan
A comprehensive implementation plan serves as a roadmap for the ERP deployment process. This plan should outline all phases of the implementation, including system configuration, data migration, testing, user training, and go-live. Establish a realistic timeline with clear milestones and deliverables. It’s important to anticipate potential risks and challenges, such as data migration issues or resistance to change, and plan for how to mitigate them.
5. Focus on Data Migration and Integration
Data migration is one of the most critical aspects of ERP implementation. Ensure that your existing data is cleaned, standardized, and validated before transferring it to the new ERP system. This process may involve removing duplicate records, correcting errors, and ensuring consistency across data sources. Proper data migration reduces the risk of errors and ensures that the new system operates smoothly from the start.
Integration with other business systems, such as CRM, HR, or supply chain management software, is also crucial. Ensure that the ERP system can seamlessly connect with your existing systems to avoid data silos and streamline operations.
6. Provide Comprehensive Training for Users
One of the most common reasons for ERP implementation failure is inadequate user training. To ensure that employees can effectively use the new system, provide comprehensive training tailored to their specific roles. Training should cover both the technical aspects of the system and how it will impact daily workflows. Offering ongoing support and resources, such as user manuals and help desks, can help employees feel more confident and reduce resistance to change.
7. Conduct Thorough Testing
Before the ERP system goes live, conduct extensive testing to identify and resolve any issues. Testing should include unit testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT). Involve end-users in the testing process to ensure that the system meets their needs and functions as expected. Address any bugs or issues that arise during testing to prevent disruptions once the system is fully operational.
8. Plan for a Smooth Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support
The go-live phase is when the ERP system is officially launched and becomes the primary system for your organization. To ensure a smooth transition, consider a phased rollout where the system is implemented in stages rather than all at once. This approach allows for adjustments and minimizes disruptions to daily operations.
Post-implementation support is critical to addressing any issues that arise after go-live. Ensure that your implementation team and vendor provide adequate support during this phase. Monitor the system’s performance, gather feedback from users, and make necessary adjustments to optimize its functionality.
9. Continuously Monitor and Optimize the System
After the ERP system is fully implemented, it’s important to continuously monitor its performance and seek opportunities for optimization. Regularly review key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure that the system is delivering the expected benefits. Stay informed about updates and new features from your ERP vendor that could enhance system capabilities. Encourage ongoing feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the system continues to meet the organization’s needs.
Conclusion
Successfully implementing an ERP system requires careful planning, strong leadership, and a commitment to change management. By following these best practices, your organization can maximize the benefits of an ERP system, improve operational efficiency, and achieve your strategic goals. Remember that ERP implementation is not a one-time project but an ongoing process that requires continuous attention and optimization.
